Calcific tendinitis
What is calcific tendinitis ?
Calcific tendinitis is the build up of calcium deposits in areas of the rotator cuff tendon. Calcium deposits have a pressure effect within the tendon, can cause a chemical reaction and can also reduce space for normal movement.
It is one of the most painful shoulder conditions and can be relentless in some unfortunate patients.
Diagnosis
A detailed history of symptoms and shoulder examination will provide many clues to the cause of the symptoms.
Further routine investigations include a shoulder X-ray and ultrasound scan to aid making the right diagnosis.
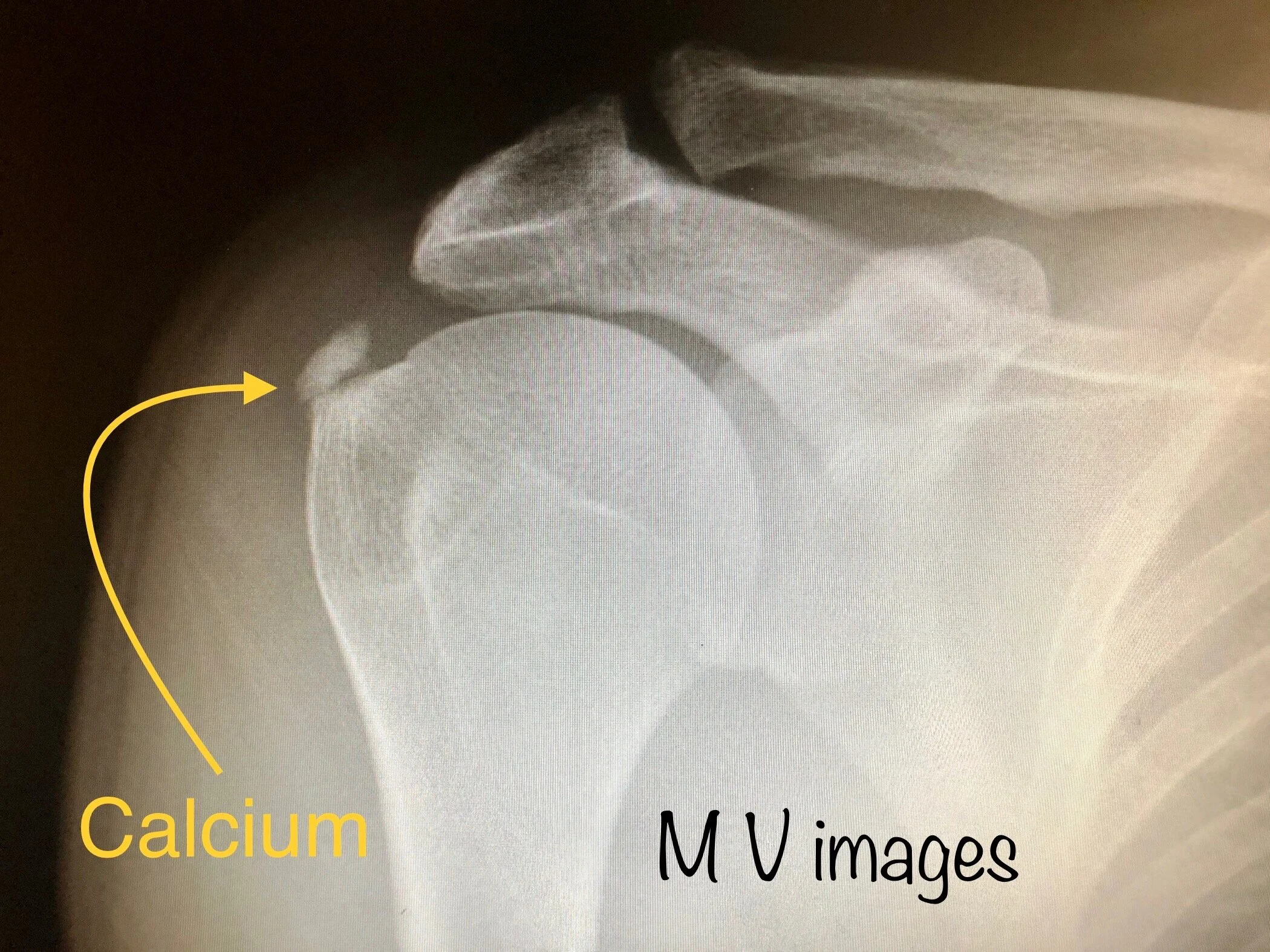
Above is an X-ray of a right shoulder in a patient with a calcium deposit embedded within the tendons that move the shoulder (rotator cuff tendons)
Treatment options
Pain medication
May help reduce pain and inflammation of the effected tendons.
Physiotherapy
Maintains shoulder movement and strength which can reduce the irritation.
Injections
Shoulder subacromial space injections - steroid injections, when correctly placed, can reduce pain and inflammation of the effected tendons.
Barbotage - A specialist radiologist can use ultrasound to inject saline around the calcium and attempt to remove it.
Surgery
Arthroscopic shoulder surgery - keyhole surgery can be performed to remove the calcium from the tendon.
Watch Mathew perform arthroscopic excision of calcium from the shoulder
Recovering after arthroscopic removal of calcium surgery
After surgery a sling is required for 2 weeks while in bed and when outdoors
Avoid getting the wounds wet until reviewed around 10-14 days following surgery
Rehabilitation with physio starts immediately
Driving is not advised for around 6-8 weeks following surgery
Returning to work depends on the nature of your job - (office based 4-6 weeks / manual work 8 weeks)
No contact sports or heavy lifting for 3 months following surgery